According to the Canadian Hearing Society, nearly 10% of all Canadians report having some form of hearing disability. That’s more than 3 million Canadians, and the numbers are expected to rise. Fortunately, 90% of this group can experience improvements in hearing and communication with adequate changes to their lifestyle and environment or properly fitted hearing aids. Hearing loss can be attributed to a variety of complications. Before you invest in hearing aids, check with a medical professional to determine the cause of your hearing loss and type of hearing loss.
Types of hearing loss
Hearing loss can be classified into three categories:
- Sensorineural hearing loss, which is caused by problems in the inner ear, sensory organ, or vestibulocochlear nerve (nerve that transmits sound to the brain)
- Conductive hearing loss, which is often a result of blockages. These may be solved without the need for hearing aids.
- Mixed hearing loss, a combination of the two above
Causes of hearing loss
The causes of permanent, inner (sensorineural) and typically temporary (conductive) hearing loss differ.
What causes sensorineural hearing loss?
- Aging
- Injury
- Excessive noise exposure
- Viral infections (such as measles or mumps)
- Shingles
- Ototoxic drugs (medications that damage hearing)
- Meningitis
- Diabetes
- Stroke
- High fever or elevated body temperature
- Ménière's disease (a disorder of the inner ear that can affect hearing and balance)
- Acoustic tumors
- Heredity
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Hypertension
Source: Starkey
What causes conductive hearing loss?
- Infections of the ear canal or middle ear resulting in fluid or pus buildup
- Perforation or scarring of the eardrum
- Wax buildup
- Dislocation of the middle ear bones (ossicles)
- Foreign object in the ear canal
- Otosclerosis (an abnormal bone growth in the middle ear)
- Abnormal growths or tumors
Source: Starkey
Treatments for hearing loss
The treatment type heavily depends on the status and health of your hearing nerve.
Sensorineural
- Irreversible or permanent hearing loss can be treated with hearing aids, or surgically treated with cochlear implants.
- In the event of a condition such as meniere’s disease or autoimmune inner ear disease, there are specific treatments. Visit hearingloss.org for more details on the various circumstances.
Conductive
- Surgery may be done in the case of an obstruction or defect
- Antibiotic or antifungal medication if there is an infection or middle fluid.
Mixed
As mixed hearing loss is caused by a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, it may require a combination of both types of treatments. Typically, hearing aids in combination of some conductive treatment to enhance hearing.
Diagnosing hearing loss
- Physical exam – doctor will look in your ear for obstruction, infection, or other structural issues
- General screening test – doctor whispers in one ear while the other is covered
- App-based hearing test – online app test
- Tuning fork tests – used to determine where the issue or damage to ear has occurred through a tuning fork “instrument”
- Audiometer tests – this is an in-depth test requiring earphones played at varying frequencies.
More info at Mayoclinic
Cost of hearing aids
Expect to pay between $1000 to $4000+ per hearing aid based on the features and capabilities.
A recent CBC article highlights secrets of the hearing aid industry in a discussion with a hearing aids manufacturer. The article notes that hearing aids cost $150 to produce on average, then are sold to retailers or audiologists for $400-$600, which is later marked up to sell to the consumer for anywhere from $1000-4000. There will be variety in pricing and mark up based on the technology as the $150 is only an average production cost. However, the article notes that the mark up is largely due to servicing from the audiologists, in which case end consumers are paying for the product and the service (checkups, cleaning, warranty, adjustments).
Factors impacting cost
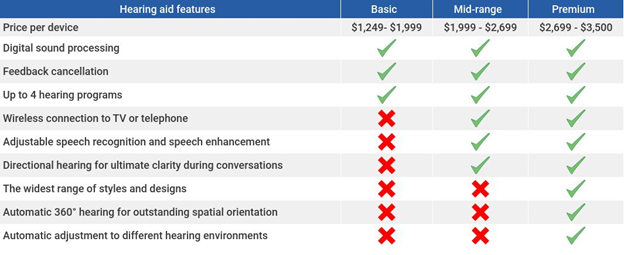
Source: Hear.com
Hearing aids costs are dependent on their features and meant to last a couple years based on the provider. There is usually servicing built into the price. Here are some features impacting price:
- Features included
- Services provided
- Continued research
- Product lifespan
- Your lifestyle – noise level in your environment
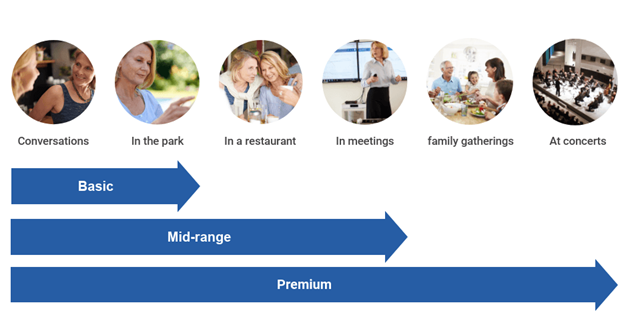
Source: Hear.com
Funding for hearing aids
There are options to have your hearing aids or hearing loss solution subsidized. Each province offers different programs. Please refer to this article for more information.
Coverage for small business owners
Hearing aids are eligible in a Health Spending Account (HSA). The cost of the hearing aids and related expenses can be deducted as a pre-tax expense through your corporation. A Health Spending Account is a cost-effective plan specifically built for small business owners to reduce their medical expenses. It turns 100% of after-tax personal medical expenses into before-tax business expenses. To see how much you can save, check out our HSA calculator – simply input your income, yearly medical expenses, and province.
A Health Spending Account is not just limited to hearing aids. There are many eligible medical expenses:
- prescription glasses
- contact lenses
- massage therapy
- physiotherapy
- prescription drugs.
See the full list of eligible Health Spending Account expenses.
Download the FREE Beginner's Guide to a Health Spending Account: